The growing demand for specialties like IT and software engineering in the West – combined with an eruption of talent in Asia – has caused ‘offshoring’ and ‘outsourcing’ to become major business buzzwords.
While many think they’re just two vague words meaning “giving your work to someone else”, this couldn’t be further from reality. The growing demand for specialties like IT and software engineering in the West – combined with an eruption of talent in Asia – has caused ‘offshoring’ and ‘outsourcing’ to become major business buzzwords.
The line can become blurred, with some even combining the two as “offshore outsourcing”, but while both share the characteristic of remote working, outsourcing and offshoring represent two utterly contrasting business models. In this piece, we’re not just looking at the differences between the two models, but also the benefits and drawbacks of each within specific types of business.
Ever considered growing your team a using remote workforce? Read on to find out whether outsourcing or offshoring is the best fit for your company.
The Evolution of Outsourcing and Offshoring
Outsourcing
The Industrial Revolution radically changed how businesses operated. Highly productive machinery and breakthrough technologies meant that companies could grow at an unprecedented rate. By the mid-1900s, many were thinking outside the box, looking for any angle to increase profits and grow their market share.
Technology was now so powerful that by simply scaling up operations, companies could leverage massive economies of scale to increase profit margins while undercutting smaller rivals. Unfortunately, this scaling usually led to a bloated and complex management structure, and with it a total lack of agility and flexibility.
Struggling with having their cake and eating it, companies decided to focus on their core business and began to ‘outsource’ their support functions. This move made it easier for companies that weren’t self-sufficient or had no internal competency to outsource to third-party vendors on a contract basis, forming the baseline of outsourcing.
Fast-forward to the 1990s. Outsourcing, as a cost-saving measure was as popular as ever. Contracts were drawn, timelines set and what seemed like smooth and hassle-free delivery of services was established.
Offshoring
The outsourcing model of the 90’s worked amazingly well, and companies were more than happy with the results. However, their expectations began to rise, and they wanted more. The one thing that outsourcing couldn’t give them was a sense of ownership, and they wanted to be in charge of the entirety of their business. Thus began the search for a business model that was cost-efficient, scalable, and gave business owners complete control and ownership. The ethics of offshoring slowly, but surely began to shift.
At the turn of the 20th century, offshoring came into play. Implementing an offshore business model meant that companies could build their team from a scalable talent pool, in a different geographical location, under the same management.

What Makes Outsourcing and Offshoring So Popular Today?
Before we dive into the pros and cons of each business model, it’s important to look at the major reasons why businesses today – both large and small – are relying on outsourcing and offshoring more than ever. Here are a few of the main ones:
1) Acute shortage of talent – A Talent Shortage Survey that was conducted in 2013 revealed that roughly 40% of US employers find it extremely difficult to fill jobs in engineering and IT. This massive talent shortage means companies have to look elsewhere to source talent.
2) Globalisation – The last decade has seen more and more firms establish a global presence. Setting up remote teams sets new trends in business on an international scale. Globalisation therefore facilitates economic growth and competitiveness, and offshoring or outsourcing is merely a consequence.
3) The need for innovation – The rapidly changing market and the need to build innovative products and services further popularized offshoring and outsourcing. When a company like Procter & Gamble outsourced their R&D activities, they managed to tie together the process of innovation and execution successfully, increasing productivity by well over 60%, in turn, generating more than $10 billion in revenue.
4) They broke the mould – While in-house businesses seemed to be working fine, the operation of such an enterprise was often rigid and frail because of the sheer amount of work that needed to be done. Manufacturing and sales became a tedious process with little to no changes. Companies began to realise that outsourcing and offshoring offered a way to break free from traditional business models and, quite possibly, generate significant returns for the business.
The Key Benefits of both Business Models
Outsourcing Benefits
Flexibility
A stand-out advantage of outsourcing is the flexibility that comes with it. Let’s say a company builds an offshore finance team. That team is permanently employed, and so even if it’s a quiet period and there’s no real work to be done, you’re still paying them for sitting around twiddling thumbs. Outsourcing, on the other hand, can be managed as little as a few hours or days at a time – they only work when you actually need them. This level of flexibility is particularly important for companies whose work is more sporadic.
Cost-effectiveness
Outsourcing is a business model that usually comes with low cost and therefore significant savings. For example, the cost of maintaining infrastructure and administration are almost completely eliminated, making it a very budget-friendly approach. According to a study conducted by Deloitte in 2016, outsourcing functions to an external party reduce the total cost by almost 45%.
Resources
There are countless business functions in every company, many of which are non-core activities; ones which don’t offer any distinct advantage over competitors. These non-core functions can distract key team members from focusing on their primary tasks, therefore wasting resources. Outsourcing to a third party means you can focus completely on your core competencies – a real boon to the company!
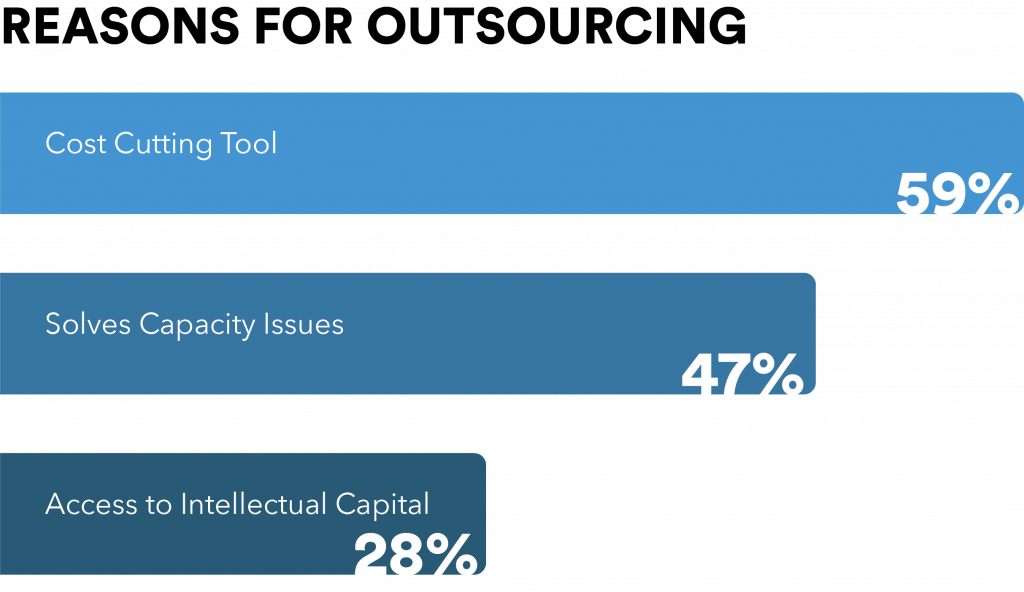
The below graph shows the major reasons why companies outsource their software development.
To know in detail read More: Outsourcing vs Offshoring Benefits